Endoscopic Temporal Bone Dissection
ENT AnatomyUse this resource in conjunction with your real-world training

Experience Summary
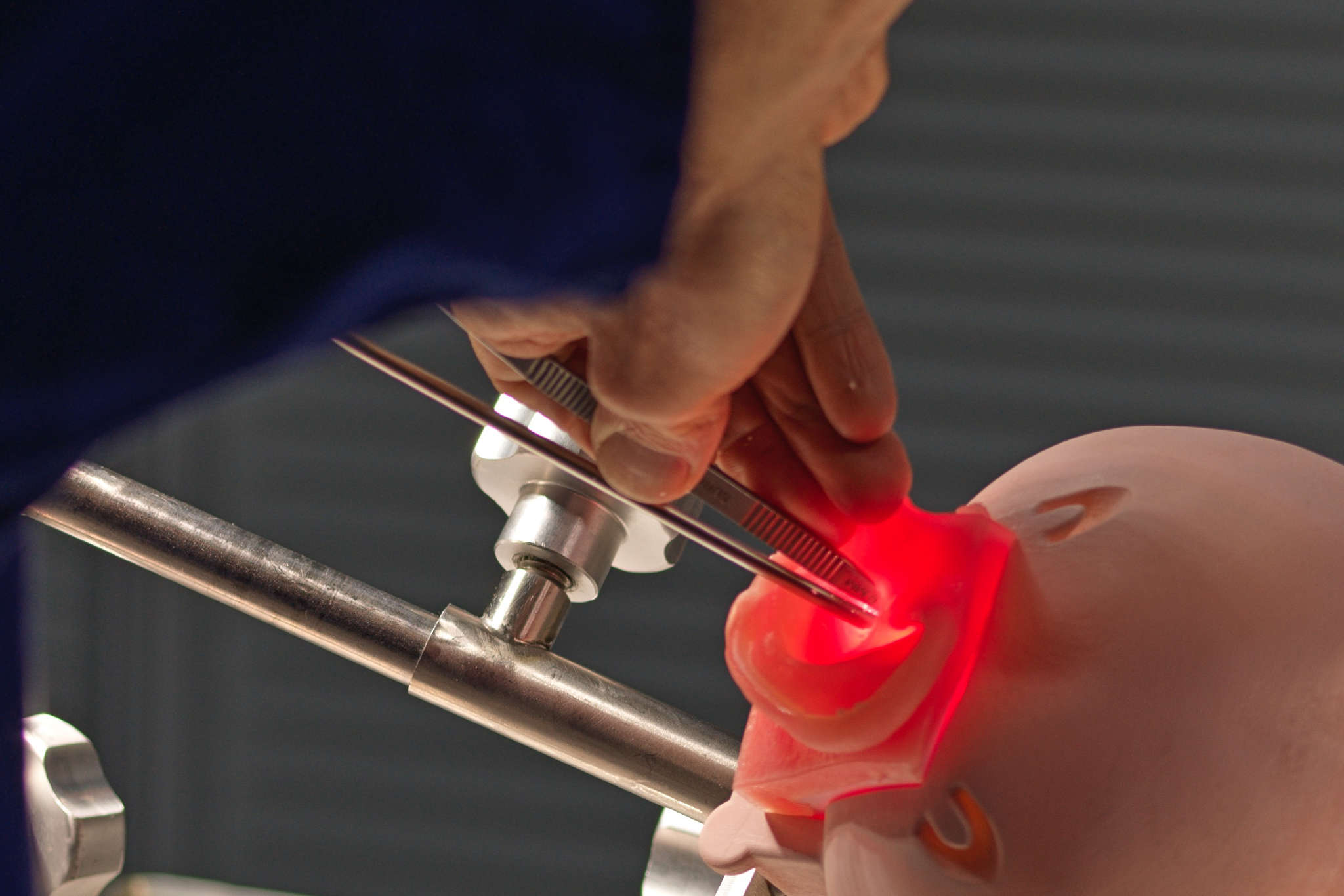
In this 360-degree video, observe a dry lab dissection of an endoscopic temporal bone using a 3D endoscope.
Clinical Context
Endoscopic temporal bone dissection is an advanced surgical training technique used by otolaryngologists to develop and refine the skills necessary for endoscopic ear surgery. With the growing adoption of minimally invasive approaches in otology, endoscopic techniques are increasingly utilised in the management of middle ear and lateral skull base pathologies. The use of cadaveric temporal bone dissection is essential for trainees and experienced surgeons to gain a comprehensive understanding of the complex anatomy of the temporal bone and to practise delicate surgical manoeuvres in a controlled, risk-free environment.
The temporal bone houses several critical structures, including the facial nerve, ossicles, cochlea, semicircular canals, internal carotid artery, jugular bulb, and dura mater. In addition, the narrow confines of the external auditory canal and middle ear cavity present significant technical challenges during surgery. Traditional microscopic techniques, while effective, offer a limited line of sight through straight pathways. In contrast, endoscopic ear surgery provides improved visualisation of hidden recesses within the middle ear, such as the epitympanum, retrotympanum, sinus tympani, and facial recess, without the need for extensive bone removal.
Endoscopic temporal bone dissection allows surgeons to develop familiarity with endoscope handling, one-handed instrument techniques, and navigation of critical anatomical landmarks under endoscopic guidance. These skills are essential when performing procedures such as endoscopic tympanoplasty, cholesteatoma removal, ossiculoplasty, and selective lateral skull base approaches. Importantly, cadaveric dissection enables the surgeon to practise identifying and preserving vital structures such as the facial nerve and ossicles, reducing the risk of complications in live surgery.
For trainees, endoscopic temporal bone dissection provides an essential educational platform to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world surgical application. By repeating dissections, surgeons develop spatial awareness and improve their dexterity with endoscopic instruments, enhancing their confidence and competence in clinical practice.
Learning Outcomes
- Observe a endoscopic temporal bone dissection.
- Understand the 3D anatomical skills required to complete this procedure.
- Observe the key steps involved in the procedure and the equipment needed to safely perform this.
External Resources
