Core Medical and Nursing Skills
There are numerous procedure based skills that healthcare providers are required to perform to deliver effective daily care for patients.
A-to-E Assessments
A‑to‑E assessments in a hospital setting refer to the systematic primary survey: Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure, that clinicians perform to quickly identify and manage life‑threatening conditions. By moving through each component in order, healthcare teams ensure that critical issues are addressed promptly before proceeding to more detailed secondary evaluations.
BLS Algorithm
The nationally agreed CPR algorithm guidelines presented as a fully immersive virtual reality tutorial.
Cervical Screening Test
Cervical screening, which used to be called smear test, is a test to check the health of the cervix and help prevent cervical cancer. It's offered to women and people with a cervix aged 25 to 64.
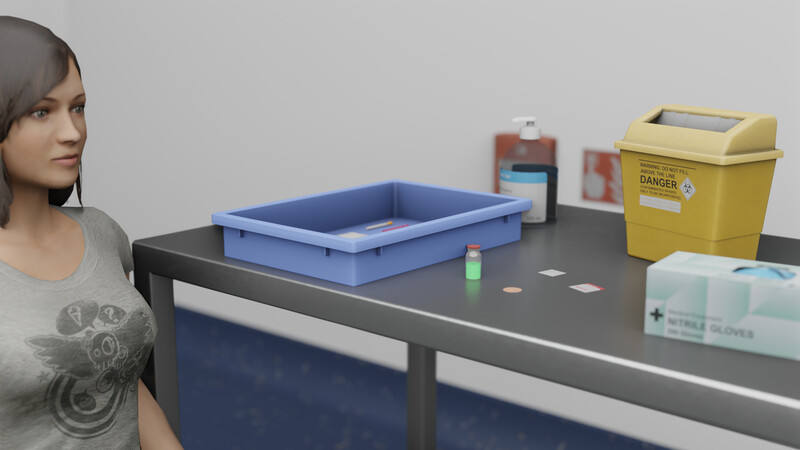

Injections / IV Access
Subcutaneous injections are the delivery method for many common medications in the hospital and community such as insulin, morphine and end-of-life medications. Proficiency here is key for delivery of daily care.
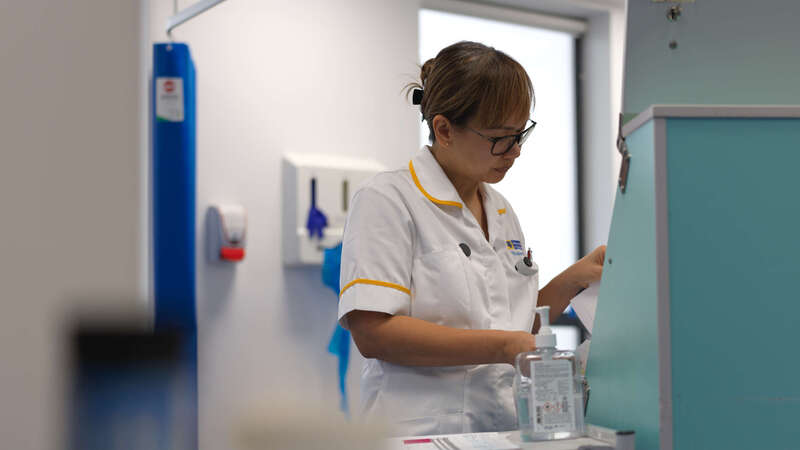

Medication Administration
Proper medical administration of drugs ensures that patients receive the correct dosage and timing, which is crucial for the effectiveness of treatment and minimizing side effects. It also helps in preventing medication errors, which can lead to serious health complications or even fatalities.

Nursing Consultation Skills in Primary Care
Primary care nurses have a wide raining set of skills in order to deal with the breath of patient presentations. Communication and empathy are central to high quality nursing care in the community.

Orthopaedic Surgical Checklists
An orthopaedic surgical checklist ensures that every step, from patient verification to instrument sterilisation, is systematically confirmed, promoting safety and consistency throughout the operation.

Professionalism
Professionalism in healthcare means consistently delivering compassionate, competent, and ethical care while respecting patient dignity and collaborating responsibly with colleagues.

Strengths Based Approach
A strengths‑based approach to communication focuses on identifying and leveraging each person's existing abilities and positive traits, fostering confidence, collaboration, and more effective, solution‑oriented interactions.
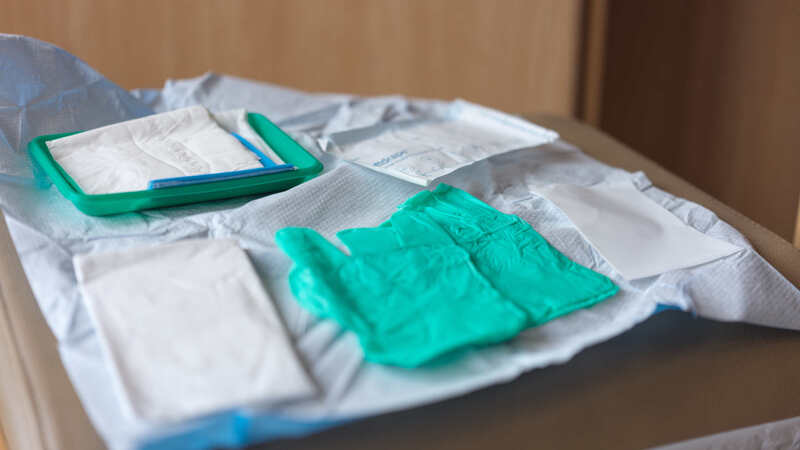

Wound Care
Proper wound care involves cleaning the area with mild soap and water, then applying an appropriate dressing to protect it from infection. Regularly monitor the wound for signs of healing or potential complications like redness or swelling.