Epley's Manoeuvre
Core ENT ProceduresUse this resource in conjunction with your real-world training

Experience Summary
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), can be debilitating for patients. In this 360-degree video, observe the steps to treat BPPV with the Epley Manoeuvre.
Clinical Context
The Epley manoeuvre is a well-established treatment for BPPV, specifically affecting the posterior semicircular canal, which is the most common site for displaced otoliths (calcium carbonate crystals). In BPPV, these crystals migrate into the semicircular canals, disturbing the normal flow of fluid and triggering vertigo when the head moves in certain positions. The Epley manoeuvre works by using a series of head and body movements to reposition these crystals back into the utricle, where they no longer cause symptoms. It is considered a safe, effective, first-line treatment for BPPV.
Counselling Points:
Before performing the Epley manoeuvre, it is important to clearly communicate the following to the patient:
- Purpose: Explain that this manoeuvre aims to reposition tiny crystals in the inner ear that have moved out of place, which is likely causing their vertigo.
- Expected Sensations: Reassure the patient that the manoeuvre may briefly reproduce their dizziness or vertigo during the movements, but this is expected and indicates the manoeuvre is working.
- Risks and Discomforts:
- Common: Temporary dizziness, nausea, mild imbalance during and shortly after the procedure.
- Rare: Vomiting, prolonged vertigo, or neck discomfort.
- Benefits: High success rate in resolving vertigo symptoms, often within one or two sessions.
- Alternatives: Watchful waiting, vestibular rehabilitation exercises, or alternative repositioning manoeuvres.
- Post-procedure Advice: Patients may feel off-balance for a few hours. Some guidelines suggest avoiding lying flat or rapid head movements for 24 hours, though evidence on strict activity restrictions is mixed.
Procedural Steps:
- Preparation:
- Explain the manoeuvre and obtain informed consent.
- Identify the affected side using the Dix-Hallpike test.
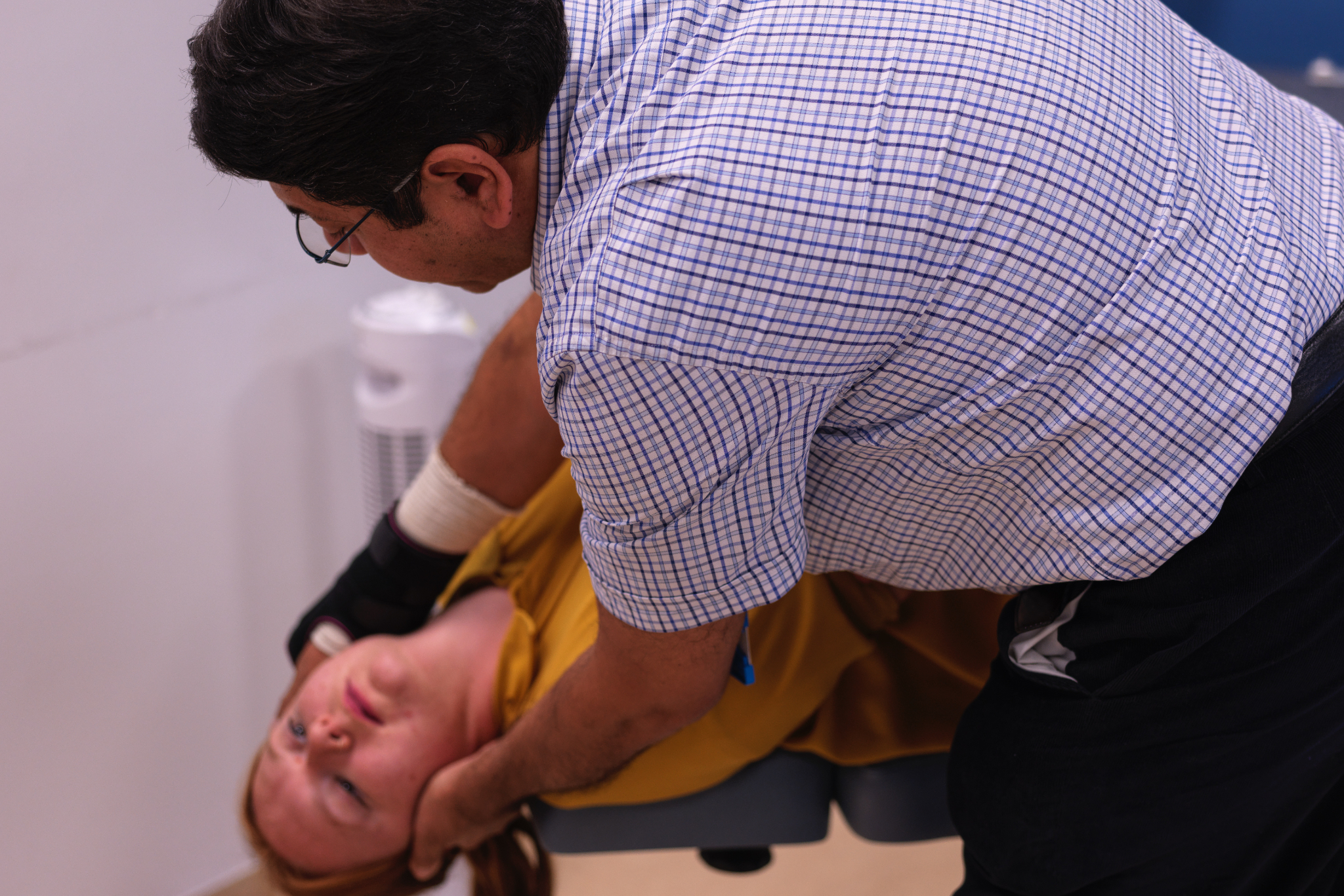
- Execution:
- The patient sits upright on an examination couch.
- The head is turned 45 degrees toward the affected side.
- While supporting the head, the patient is quickly laid back so their head extends 20-30 degrees below the horizontal plane, maintaining the 45-degree head turn.
- Hold this position for 30-60 seconds, observing for nystagmus and vertigo.
- Next, the head is rotated 90 degrees toward the unaffected side, and held for another 30-60 seconds.
- The patient then rolls onto their side, turning the head another 90 degrees, so they are looking downward at a 45-degree angle. Hold for 30-60 seconds.
- Finally, the patient is assisted back to a sitting position.
- Post-procedure:
- Reassess symptoms.
- The manoeuvre may be repeated if symptoms persist.
- Provide advice and arrange follow-up if needed.
Learning Outcomes
- Understand how to treat BPPV.
- Understand the positioning of the patient relative to the examiner, and the subsequent movements required to perform the Epley Manoeuvre.
- Understand the importance of counselling the patient appropriately prior to a potentially uncomfortable procedure.
External Resources
