Blunt Dissection Chest Drain Insertion
Acute Care Common Stem (ACCS)Use this resource in conjunction with your real-world training

Experience Summary
In this 360-degree video, observe the procedure for inserting an open (or blunt dissection) chest drain for a patient with a large haemopneumothorax.
Clinical Context
Chest drain insertion using blunt dissection is a traditional and widely used method for inserting an intercostal catheter into the pleural space. It is especially indicated in emergency situations or when draining large volumes of air, blood, pus, or fluid, such as in cases of tension pneumothorax, large pleural effusion, haemothorax, or empyema. This technique allows the insertion of larger-bore chest tubes (typically 20–36 Fr), making it suitable for trauma, massive effusions, or when there is a high risk of tube blockage.
Blunt dissection is often preferred in unstable patients or trauma settings because it offers tactile feedback and reduces the risk of injury to underlying structures when performed correctly.
Steps of Performing Chest Drain Insertion via Blunt Dissection:
- Preparation and Consent:
- Confirm indication and side of pathology with clinical assessment and imaging (e.g., chest X-ray or ultrasound).
- Obtain informed consent where possible, explaining risks such as bleeding, infection, and organ injury.
- Gather sterile equipment: chest drain kit, large-bore chest tube, sterile gloves, gown, antiseptic, drapes, scalpel, artery forceps, and suture materials.
- Patient Positioning and Monitoring:
- Position the patient semi-upright or supine with the arm on the affected side raised above the head or behind the neck to expose the axillary region.
- Attach monitoring (ECG, pulse oximetry) and provide supplemental oxygen as needed.
- Site Selection and Anaesthesia:
- Identify the "safe triangle": bordered by the anterior axillary line, lateral edge of pectoralis major, and the horizontal line of the nipple (approximately 4th–5th intercostal space).
- Clean the area with antiseptic and apply sterile drapes.
- Infiltrate local anaesthetic through the skin, subcutaneous tissue, intercostal muscles, and down to the pleura.
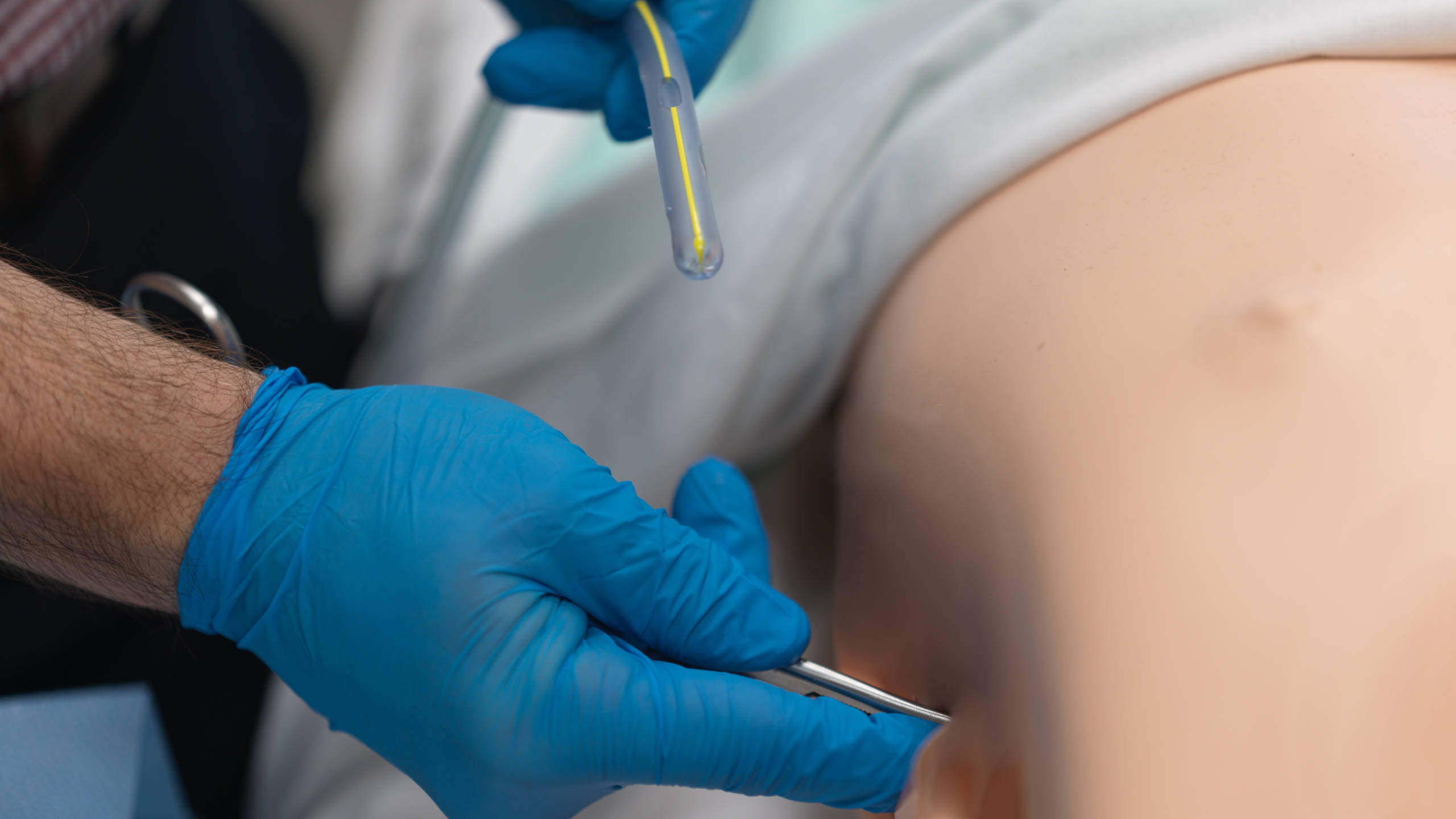
- Blunt Dissection:
- Make a 2–3 cm horizontal skin incision just above the rib to avoid the neurovascular bundle.
- Use curved artery forceps to bluntly dissect through subcutaneous tissue and intercostal muscles.
- Pierce the parietal pleura and widen the opening with a finger (finger sweep) to confirm entry and exclude adhesions.
- Tube Insertion and Securing:
- Insert the chest tube into the pleural space, directing it appropriately (posteriorly and superiorly for air, posteriorly and inferiorly for fluid).
- Confirm placement with a finger sweep, secure with sutures, and apply an occlusive dressing.
- Post-Insertion Care:
- Connect to an underwater seal drain.
- Confirm position with a chest X-ray.
- Monitor output, respiratory function, and for complications.
Learning Outcomes
- Observe the procedure of inserting a chest drain using an open technique.
- Understand the procedural steps of inserting a chest drain using an open technique.
- Understand the equipment required to insert a chest drain using an open technique.
- Understand the key safety points in inserting a chest drain using an open technique.
External Resources
