Tracheostomy and Airway Management
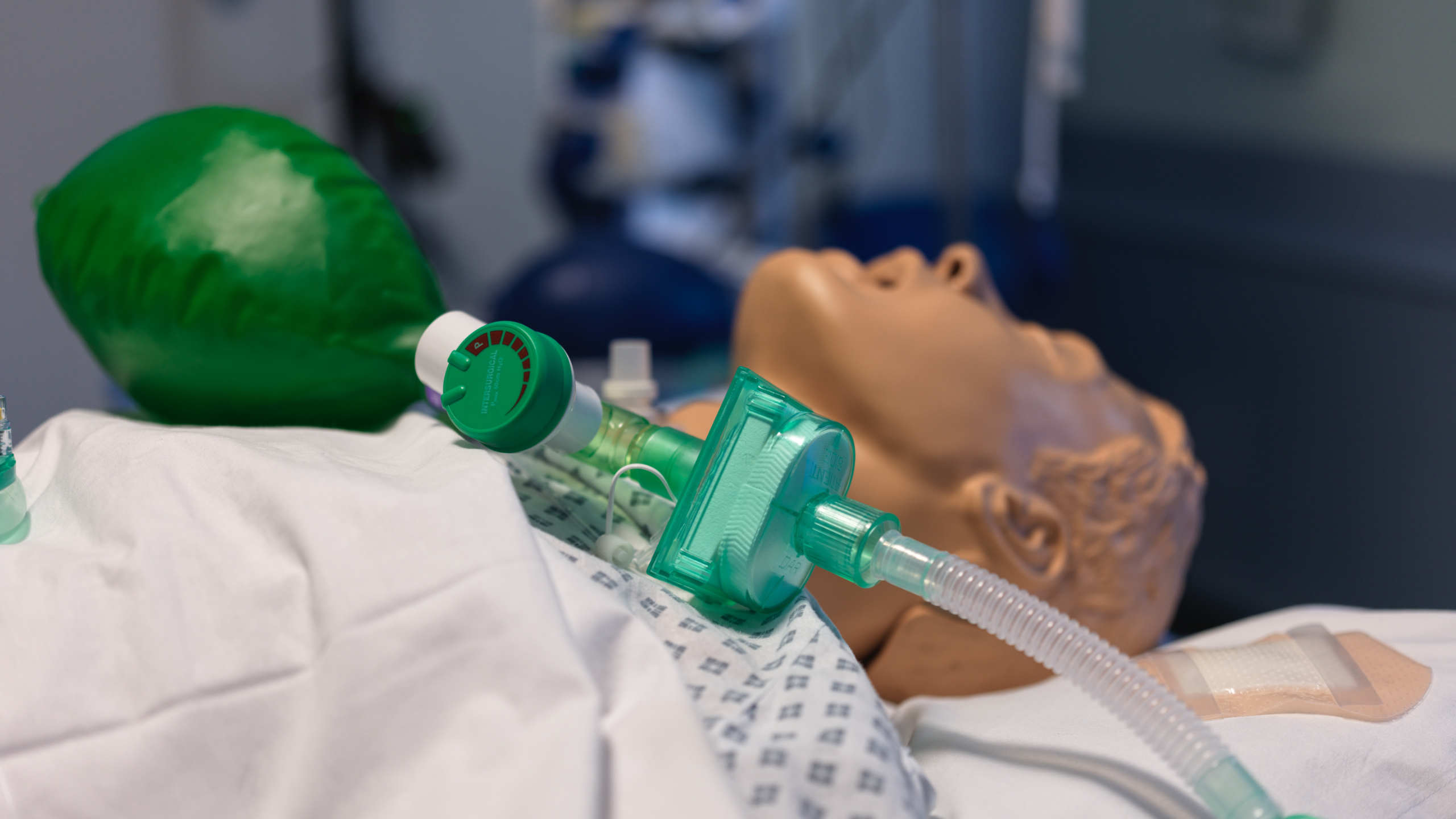
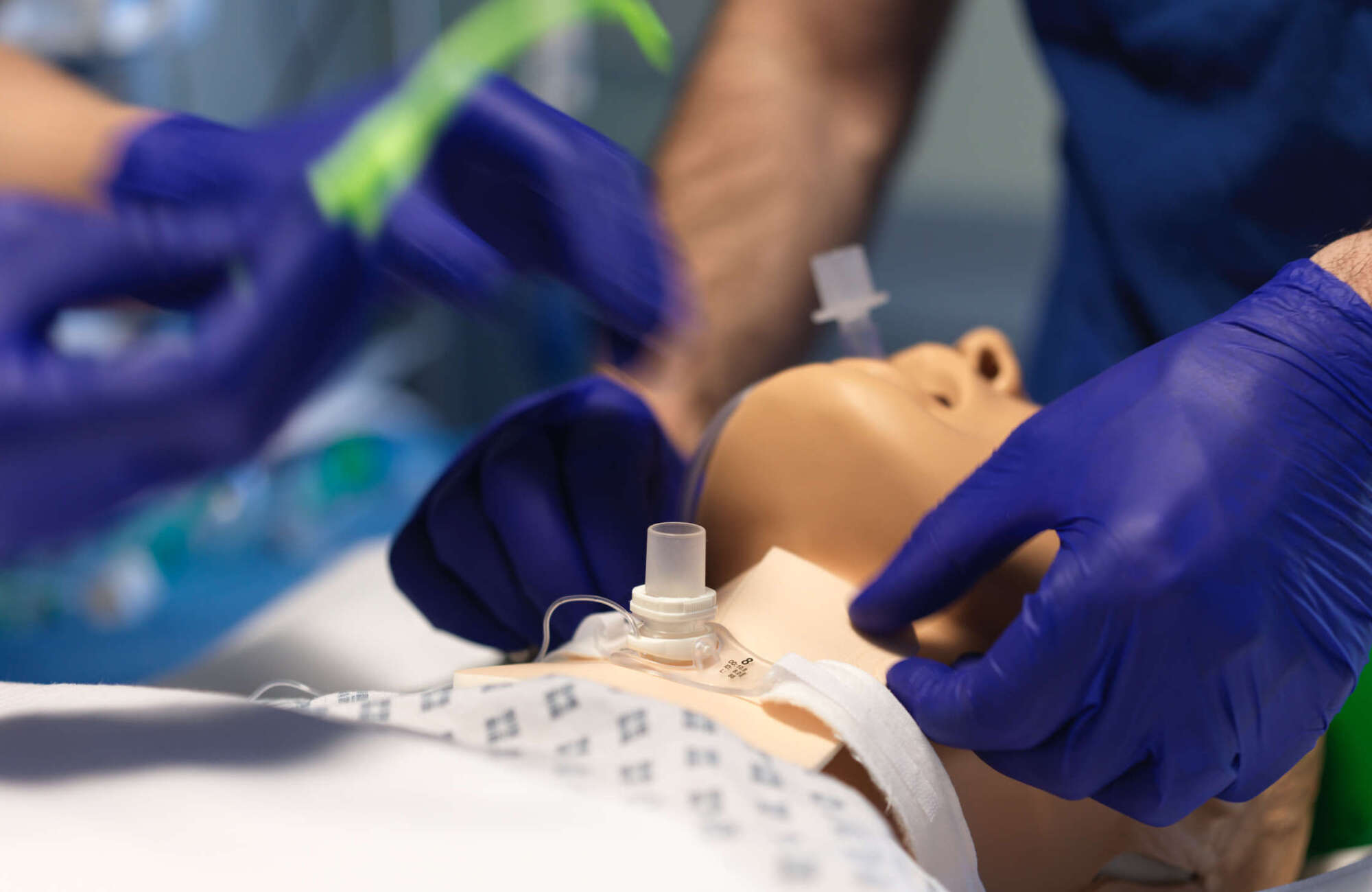
A tracheostomy is a surgical procedure that involves creating an opening in the neck to provide direct access to the trachea, bypassing the upper airway. This procedure is commonly performed in patients who require long-term mechanical ventilation, have upper airway obstructions, or suffer from conditions that impair their ability to breathe effectively.
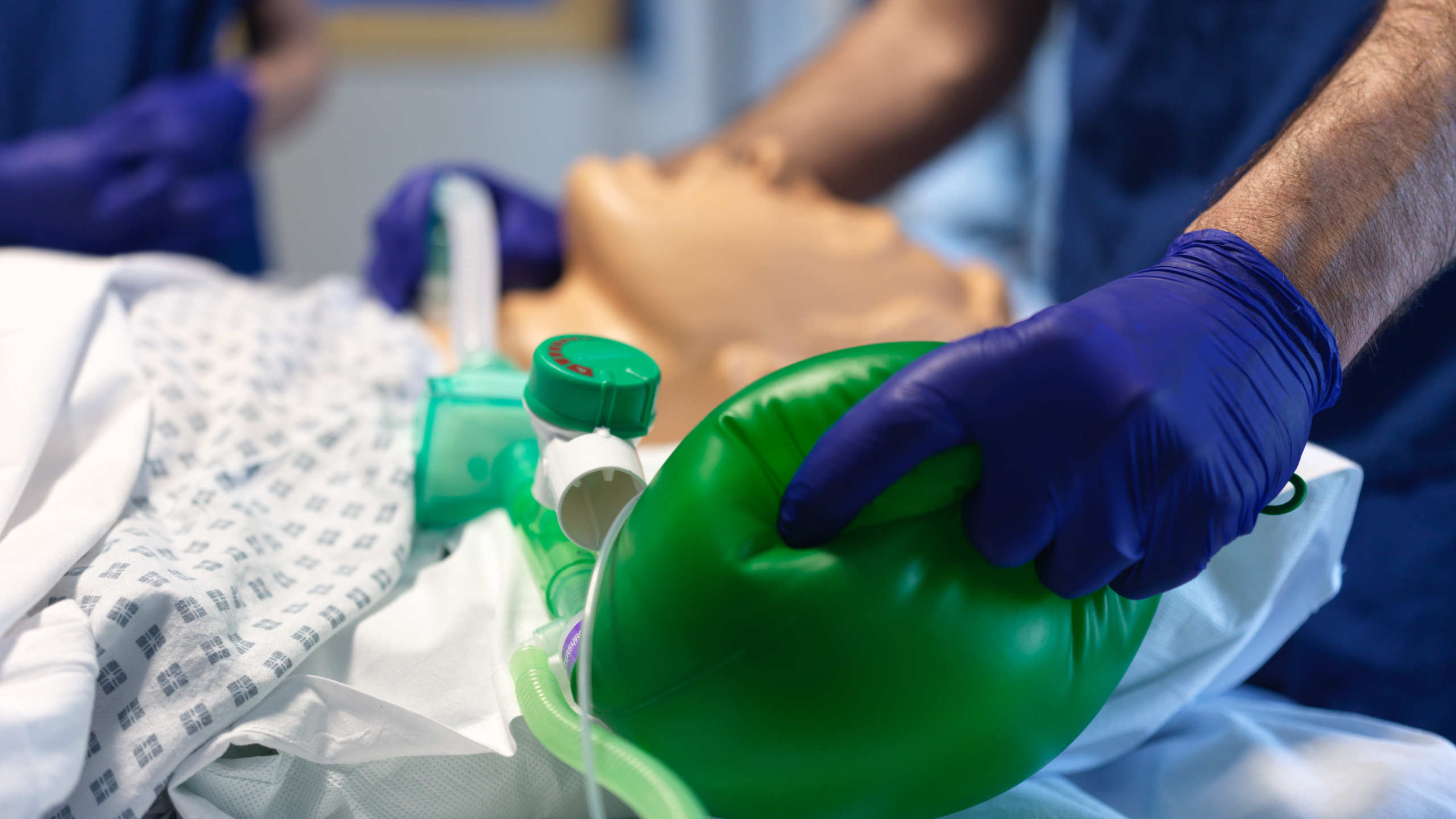
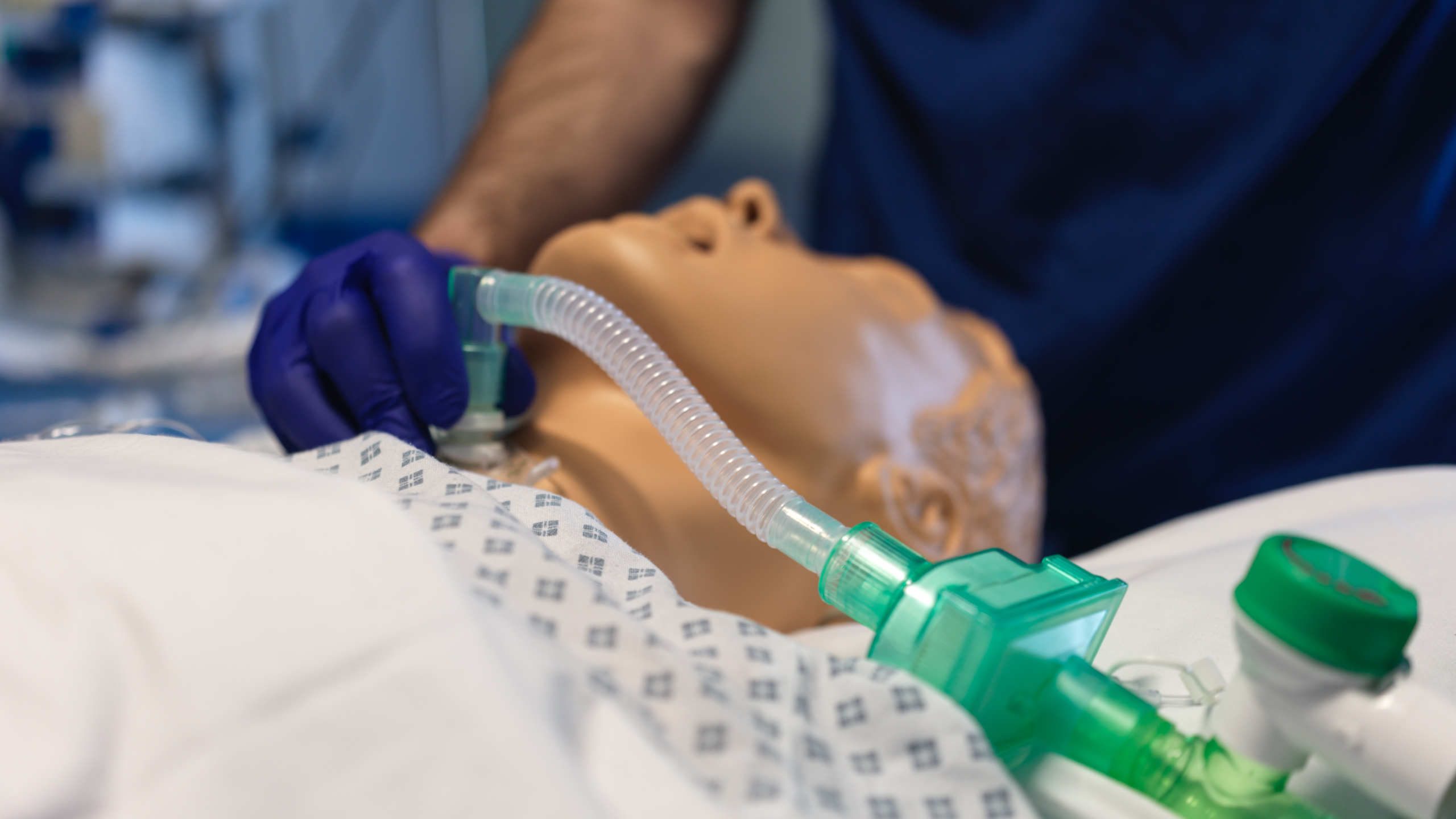
The primary goal of a tracheostomy is to facilitate secure and efficient airway management, allowing for easier breathing, improved oxygenation, and reduced reliance on invasive ventilatory support. Post-operatively, careful airway management is crucial to ensure the patient's safety and comfort. This involves regular monitoring of the tracheostomy site for signs of infection or bleeding, frequent suctioning to remove mucus and secretions that could obstruct the airway, and ensuring the tracheostomy tube is properly positioned and secured. Additionally, healthcare providers must be vigilant in assessing the patient's respiratory status, adjusting ventilator settings as needed, and providing humidification to prevent the airway from drying out. Proper care and management of a tracheostomy can significantly improve a patient's quality of life and reduce the risk of complications, making it an essential intervention in critical care settings.